- Categories:
- Equipment
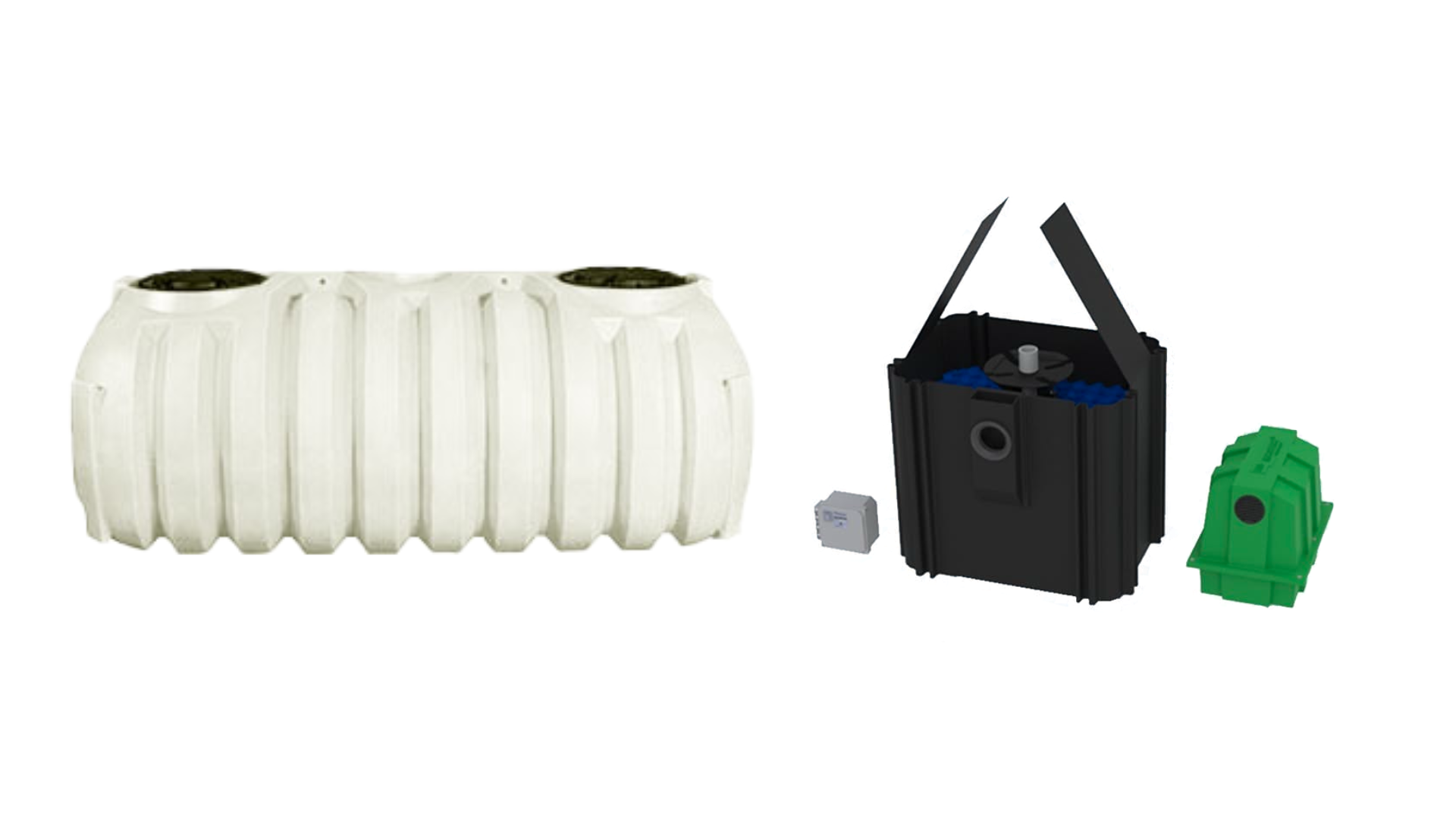

Septic Tank vs. ATU
Installing a septic tank and an aerobic treatment unit (ATU) are two different approaches to managing household wastewater in areas without access to centralized sewer systems. Both systems treat and dispose of effluent, but they do so in different ways and with varying levels of treatment efficiency. Here are the core differences between them:
Septic Tank Systems:
-
Anaerobic Process: Septic tanks work using an anaerobic process, which means that they operate without oxygen. Waste is broken down by bacteria that thrive in oxygen-free environments.
-
Components: A septic system generally consists of a septic tank and a drainfield (also known as a leach field or absorption field).
-
Function: In the tank, solids settle to the bottom to form sludge, while fats, oils, and greases float to the top to form a scum layer. The middle layer of relatively clear water then flows out to the drainfield, where it is further treated by the soil.
-
Treatment Efficiency: Septic tanks primarily remove solids and perform basic treatment of effluent, reducing organic content; however, the effluent quality is typically lower than that produced by an ATU.
-
Maintenance: It requires less frequent maintenance than an ATU but will periodically need pumping to remove accumulated solids.
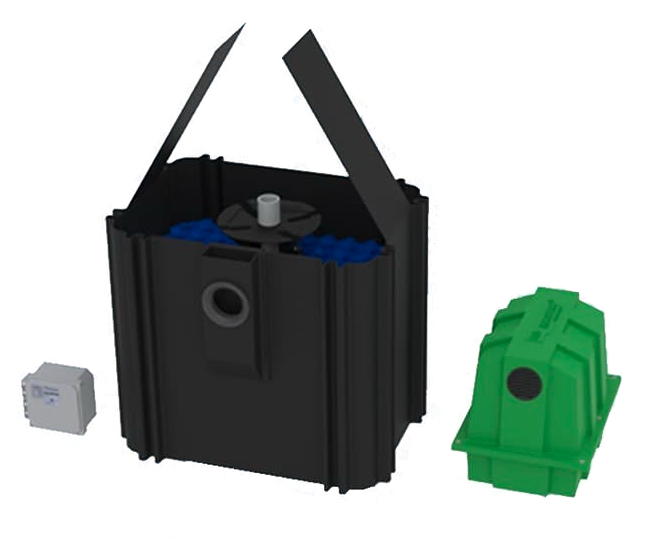

Aerobic Treatment Units:
-
Anaerobic Process: ATUs use an aerobic process, employing oxygen to support the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter much more thoroughly than anaerobic bacteria.
-
Components: ATUs consist of several chambers or tanks, including an aeration chamber where air is injected or circulated through the wastewater.
-
Function: The forced introduction of air enhances the breakdown of waste in the effluent, reducing the organic matter content and pathogens significantly. The treated water can then be discharged to a smaller drainfield or in some regions, may be suitable for surface irrigation or other uses.
-
Treatment Efficiency: The effluent from an ATU is typically clearer and has fewer pathogens and organic materials than that from a traditional septic tank, which can be beneficial for the environment and in areas with high groundwater tables or small lot sizes.
-
Maintenance: ATUs require more maintenance, including regular checks and service of mechanical parts like pumps and aerators.
When deciding between these two systems, one should consider factors such as regulatory requirements, site conditions, installation and operating costs, maintenance requirements, and the desired quality of effluent treatment. Local environmental regulations may also dictate or recommend a particular system type based on the protection of groundwater and surface water quality.
Horizon has is your #1 source in South Florida for septic supplies, including septic tanks, septic pumps, septic covers and all size ATU. Call your local Horizon today for pricing and delivery information for your next job.